Introduction
In the pursuit of a radiant smile, there's nothing more perplexing than diligently brushing your teeth every day, only to be greeted by persistent yellowing. Let's delve into the common culprits behind tooth discoloration and unveil practical solutions for reclaiming your pearly whites.
Importance of oral health and maintaining white teeth
Embarking on the journey to dazzling pearly whites involves more than just brushing. Oral hygiene is the cornerstone, and a diligent routine paired with a sonic toothbrush can make a significant impact. Paying attention to what goes into your mouth matters – a balanced, teeth-friendly diet can combat discoloration.
Yet, even the most diligent routines require a professional touch. Regular dental check-ups act as preventive measures, ensuring potential issues are nipped in the bud. For those seeking an extra gleam, cautiously chosen teeth whitening products can be a game-changer. In this exploration of oral health, discover the keys to maintaining a brilliantly white smile.
Understanding Tooth Discoloration: Unraveling the Causes, Impact, and Prevention
Tooth discoloration can result from various factors, with tobacco use and medications being common culprits. In this exploration, we'll delve into the causes, the impact of these contributors on tooth color, and effective prevention strategies.
Common Causes of Tooth Discoloration
Understanding why teeth may lose their natural whiteness is crucial. Tobacco use, a prominent factor, stains teeth due to the tar and nicotine. Additionally, certain medications, like tetracycline and antihypertensive drugs, can contribute to discoloration. Other influences include aging, poor dental hygiene, and specific foods and drinks.
How Factors Contribute to Discoloration
Tobacco products contain compounds that adhere to tooth enamel, resulting in stubborn stains. Medications, especially when taken during tooth development, can cause intrinsic discoloration. Tetracycline, for instance, may discolor teeth when administered to children. The cumulative impact of these factors often leads to noticeable changes in tooth color.
Impact of Tobacco Use and Medications
Tobacco's impact on tooth discoloration extends beyond cosmetic concerns, influencing overall oral health. The tar and nicotine in tobacco products create resilient stains on tooth enamel, resisting typical cleaning methods. Beyond aesthetics, tobacco use heightens the risk of gum disease, as the chemicals irritate and compromise gum health. Stained teeth often signal underlying dental issues, contributing to cavities, plaque, and bad breath. Additionally, the persistent exposure to tobacco compounds diminishes the effectiveness of professional teeth-whitening treatments, requiring more frequent interventions.
The repercussions of tobacco on oral health are not confined to the mouth. The habit's association with systemic diseases underscores its broader impact on overall well-being. Breaking free from tobacco is not only a step towards a brighter smile but also a crucial decision for comprehensive oral care and improved health. Seeking professional guidance and adopting cessation strategies are essential measures in mitigating the adverse effects of tobacco on both dental aesthetics and broader health considerations.
The impact of medications on tooth discoloration is a nuanced aspect of oral health that warrants attention. Certain medications, when administered during tooth development or taken for prolonged periods, can lead to intrinsic discoloration – a phenomenon that affects the internal structure of the tooth. Tetracycline, an antibiotic, is a notable example. When children take tetracycline, it can cause intrinsic staining that manifests as a grayish or brownish hue on the teeth.
Other medications, such as antihypertensive drugs and antipsychotics, may induce tooth discoloration as a side effect. These medications can affect the enamel, leading to changes in color over time. The impact varies among individuals and is influenced by factors like dosage, duration of use, and individual susceptibility.
Addressing and Preventing Discoloration
To counteract tooth discoloration, quitting tobacco is a significant step. Regular dental check-ups allow professionals to identify early signs and recommend suitable preventive measures. Maintaining good oral hygiene, including regular brushing and flossing, helps prevent external stains.
For medication-induced discoloration, consulting with a healthcare professional to explore alternatives or manage side effects is essential.
Extrinsic Stains: Unveiling Causes, Solutions, and Brightening Solutions
Extrinsic stains are often influenced by the foods we consume, beverages we indulge in, and certain oral habits. In this exploration, we'll review the causes of extrinsic stains and assess effective treatment options.
Understanding Extrinsic Stains
Extrinsic stains, primarily caused by external factors, find their roots in our dietary choices and lifestyle habits. Foods like berries, beverages such as coffee or red wine, and habits like smoking can contribute to discoloration over time.
The impact of these external agents on tooth enamel leads to the noticeable yellowing that diligent brushing alone might not fully address.
Treatment Options for Extrinsic Stains
The good news is that managing extrinsic stains involves accessible and effective solutions. Practicing proper oral hygiene is fundamental; regular brushing and flossing play a pivotal role in preventing and minimizing these stains.
Professional dental cleanings further enhance the arsenal against extrinsic discoloration by tackling hard-to-reach areas and stubborn deposits.
The Role of Oral Hygiene
Maintaining a consistent and thorough oral hygiene routine becomes the cornerstone of preventing extrinsic stains. Brushing after consuming stain-prone foods or beverages, along with flossing, helps mitigate the impact of external factors on your tooth enamel.
This proactive approach significantly contributes to a brighter and healthier smile.
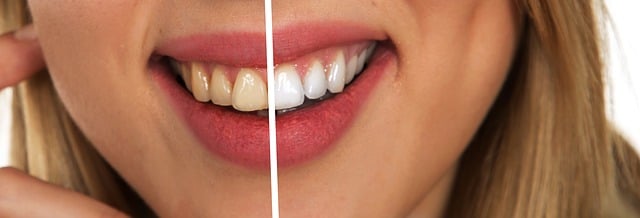
Teeth Whitening Treatments for Extrinsic Stains
For those seeking a radiant transformation, various teeth whitening treatments prove effective in combating extrinsic stains. Procedures like ZOOM and bleach trays are popular options, offering professional-grade solutions to lighten tooth discoloration. These treatments penetrate enamel, breaking down stains and unveiling a brighter, revitalized smile.
Causes of extrinsic stains (tobacco products, coffee, tea, etc.)
Such external discolorations, originating from tobacco products, coffee, tea, and certain foods, gradually make their mark on enamel.
1. Tobacco Products: The nicotine and tar in tobacco contribute significantly to extrinsic stains. These substances adhere to enamel, leaving an unmistakable yellow tint over time.
2. Coffee and Tea: The rich, dark hues in coffee and tea contain chromogens, pigment-producing substances that latch onto teeth. Regular consumption can result in noticeable staining, especially if oral hygiene is not diligently maintained.
3. Teeth-Staining Foods: Certain foods, like berries, soy sauce, and tomato-based sauces, are culprits in extrinsic staining. Their vibrant colors indicate the presence of chromogens that adhere to enamel surfaces.
Effects of extrinsic stains on tooth enamel
Extrinsic stains, though superficial, can significantly impact the appearance of tooth enamel. These stains accumulate on the outer layer of the teeth, causing discoloration that is often perceived as yellowing. While extrinsic stains don't penetrate the deeper layers of the tooth, they can create a visual contrast that diminishes the overall aesthetics of the smile.
Surface Discoloration
Extrinsic stains manifest as surface discoloration, altering the translucency and vibrancy of tooth enamel. The accumulation of pigmented particles from foods, beverages, and habits like smoking can lead to noticeable yellow or brown spots on the teeth. This surface-level discoloration can be particularly bothersome, as it directly affects the smile's cosmetic appeal.
Impact on Confidence
The visible effects of extrinsic stains can impact an individual's confidence and self-esteem. A discolored smile may lead to self-consciousness, affecting social interactions and even inhibiting one's willingness to smile openly. Understanding how these stains affect tooth enamel is crucial for individuals seeking solutions to enhance both oral health and the aesthetics of their smile.
Intrinsic Stains: Unraveling the Deeper Shades of Tooth Discoloration
While diligent brushing is a cornerstone of oral care, persistent yellowing may be due to intrinsic stains—deep-seated discoloration within the tooth. Causes vary, encompassing tooth trauma, certain medications, excessive fluoride intake, and genetic conditions.
Causes of Intrinsic Stains:
-
Tooth Trauma: Previous injuries can cause the tooth to darken due to internal bleeding or changes in dentin.
-
Medication: Certain medications, particularly during tooth development, may lead to intrinsic discoloration.
-
Fluoride Intake: Excessive fluoride exposure, especially during tooth development, can result in intrinsic staining.
-
Genetic Conditions: Inherited conditions like amelogenesis imperfecta or dentinogenesis imperfecta contribute to intrinsic discoloration.
Dental Treatments for Intrinsic Stains:
-
Teeth Whitening: Professional whitening treatments use bleaching agents to lighten intrinsic stains effectively.
-
Dental Veneers: Thin porcelain shells cover the tooth's front surface, concealing intrinsic discoloration and providing a natural appearance.
-
Composite Bonding: Tooth-colored resin is applied to the tooth, effectively masking intrinsic stains.
Limitations of Regular Brushing:
While daily brushing is vital, intrinsic stains often reside beyond the tooth's surface. Regular brushing may not suffice, necessitating advanced whitening treatments to reach deeper layers of the tooth.
The Need for Advanced Whitening Treatments:
To combat intrinsic stains comprehensively, consider professional teeth whitening procedures that penetrate deeper layers, addressing discoloration at its source. Embrace these advanced treatments for a brighter, whiter smile that reflects your commitment to optimal dental care.
In the pursuit of a radiant smile, understanding intrinsic stains and opting for tailored dental treatments ensures a confident, luminous grin that goes beyond surface-level care.
The role of tooth enamel in tooth color
Understanding Tooth Enamel: A Protective Guardian
To comprehend the interplay of tooth color, we must first acknowledge the pivotal role of tooth enamel. This translucent outer layer serves as a resilient shield, protecting teeth from external factors and stains. Yet, despite its durability, enamel is not impervious to wear.
Wearing Down Over Time: Unveiling Dentin
As the stalwart guardian, tooth enamel gradually weathers the storms of daily life. Frequent use, acidic foods, and abrasive brushing contribute to its erosion. This wear and tear, over time, unveil the underlying dentin layer. Unlike enamel, dentin carries a natural yellow hue, influencing the overall color perception of our teeth.
Genetics and Tooth Color Variations
Genetics introduces a captivating dimension to tooth color. It dictates not only the inherent color of dentin but also determines the thickness and translucency of enamel. Individuals may inherit genes that lead to thinner or more translucent enamel, resulting in a spectrum of tooth colors within a family.
Embracing Natural Variation
Yellower teeth, often a consequence of genetic factors, shouldn't be stigmatized. The beauty of our smiles lies in the natural variations influenced by our genetic makeup. Embracing these differences fosters a positive perspective on dental aesthetics.
Yellower Teeth, Healthy Smiles
Contrary to common misconceptions, having yellower teeth doesn't necessarily indicate poor oral health. Dental health is a nuanced combination of various factors beyond color. Regular oral care, including proper brushing and dental check-ups, remains paramount for overall oral health.
In navigating the intricate relationship between tooth enamel, genetics, and tooth color, we gain a deeper appreciation for the uniqueness of each individual's smile. Embrace the diversity, prioritize oral care, and celebrate the natural beauty of your teeth.
Explanation of tooth enamel composition and function
Tooth enamel, the outermost layer of our teeth, is a remarkable protector. Composed primarily of minerals, including hydroxyapatite, it forms a resilient shield against daily wear and tear. Its crucial function extends beyond aesthetics, acting as a barrier against bacteria and sensitivity.
As we age, the enamel undergoes natural wear, thinning over time. Aggressive brushing accelerates this process, leading to enamel erosion. Acidic foods and drinks further contribute, softening enamel and making it susceptible to erosion.
Enamel erosion, if unchecked, can result in tooth discoloration. The thinning enamel exposes the underlying dentin, which is naturally yellowish, influencing the overall color of the teeth.
Minimizing enamel wear is essential. Opt for a soft-bristled toothbrush, gentler brushing techniques, and toothpaste designed for enamel protection. Reduce acidic food and beverage intake, and consider using a straw when consuming acidic drinks to minimize contact with teeth.
How thinning or erosion of enamel can lead to yellowing
The yellowing of teeth, despite regular brushing, often stems from the thinning or erosion of enamel. Enamel, the protective outer layer, can diminish due to aging, aggressive brushing, and acidic foods. As it wears away, the yellowish dentin layer beneath becomes visible, causing teeth to lose their natural luster.
Causes of Enamel Thinning and Yellowing:
- Aging: Over time, natural wear and tear contribute to enamel thinning, making the dentin layer more apparent.
- Aggressive Brushing: Brushing vigorously may seem effective, but it can accelerate enamel erosion, revealing the yellow hues of the dentin underneath.
- Acidic Foods: Consuming acidic foods and beverages regularly can weaken enamel, leaving teeth susceptible to yellowing over time.
Preventive Measures to Minimize Enamel Thinning:
- Fluoride Toothpaste: Choose a fluoride toothpaste to strengthen enamel and provide an extra layer of defense against yellowing.
- Gentle Brushing: Adopt a gentler brushing technique to safeguard enamel. Soft-bristled brushes and a delicate touch are key.
- Avoid Acidic Foods and Drinks: Limit the intake of acidic foods and drinks to mitigate enamel erosion, preserving the natural whiteness of your teeth.
Tooth decay and its impact on tooth color
Tooth decay, a common oral health concern, significantly influences the color of our teeth. The effects of decay extend beyond mere cavities, often causing noticeable discoloration. Here's how tooth decay contributes to changes in tooth color:
-
Enamel Weakness: Tooth decay weakens the protective enamel layer, making it more susceptible to stains and discoloration. As enamel deteriorates, the natural whiteness of teeth diminishes, revealing the underlying dentin.
-
Bacterial Invasion: Decay invites harmful bacteria into the oral environment. These bacteria produce acids that not only erode enamel but also contribute to the formation of yellow or brown spots on the teeth. This bacterial intrusion disrupts the harmony of a vibrant smile.
-
Plaque Accumulation: The accumulation of plaque, a sticky film of bacteria, sugars, and saliva, plays a pivotal role in tooth discoloration. Plaque adheres to weakened enamel, fostering an environment where bacteria thrive, leading to further discoloration.
-
Overall Dullness and Darkening: As decay progresses, teeth may lose their natural luster and appear overall dull. The darkening of enamel is a consequence of both enamel erosion and the accumulation of debris within microscopic pits and cracks.
Relationship between dental caries and discoloration
Understanding why teeth may appear yellow, even with regular brushing, involves exploring the intricate link between dental caries and tooth discoloration. Dental caries, commonly known as tooth decay, is a primary contributor to discoloration. As the enamel breaks down due to decay, the natural white appearance diminishes, revealing the underlying dentin, which has a yellowish tint.
Poor oral hygiene amplifies this process. Inadequate brushing and flossing allow bacteria to thrive, leading to the formation of plaque and tartar. These buildups not only contribute to dental caries but also intensify tooth discoloration. Consistent and thorough oral care is crucial in preventing the progression of decay and maintaining a bright smile.
Moreover, the consumption of certain foods and drinks plays a dual role in dental caries and discoloration. Sugary and acidic foods create an environment conducive to bacterial growth and enamel erosion, fostering tooth decay. Additionally, beverages like coffee, tea, and red wine contain pigments that can stain teeth over time, further exacerbating discoloration.
In essence, the relationship between dental caries and tooth discoloration is intricate. Prioritizing meticulous oral hygiene practices and being mindful of dietary choices are key steps in preserving the natural vibrancy of your smile while safeguarding against both dental caries and unwanted discoloration.
Acidic food consumption and its effect on enamel integrity
Have you ever wondered why despite brushing daily, your teeth seem to retain a yellow tint? The culprit might be lurking in your diet. Acidic foods, such as citrus fruits, sodas, and certain sauces, can compromise enamel integrity, leading to tooth discoloration and heightened sensitivity.
Effects of Acidic Foods on Tooth Enamel
Acidic foods and drinks create an acidic environment in your mouth, softening the enamel—the protective outer layer of your teeth. Over time, frequent exposure to acidity can erode this enamel, exposing the underlying dentin and causing teeth to appear yellow. Additionally, weakened enamel contributes to heightened tooth sensitivity, making hot or cold foods and beverages uncomfortable.
Protective Measures for Enamel Erosion
To safeguard your enamel and maintain a bright smile:
-
Moderation is Key: Limit the consumption of highly acidic foods and drinks. Opt for water or milk as alternatives to acidic beverages.
-
Use a Straw: When indulging in acidic drinks, using a straw can minimize direct contact with your teeth, reducing the risk of enamel erosion.
-
Rinse with Water: After consuming acidic foods, rinse your mouth with water to neutralize acidity and help restore a balanced pH level.
-
Wait to Brush: Wait at least 30 minutes after consuming acidic foods before brushing. Brushing immediately can further weaken softened enamel.
-
Choose Low-Acidity Options: When possible, choose low-acidity fruits and foods. Incorporate enamel-friendly options like dairy products, nuts, and non-acidic fruits into your diet.
Dental Care for Enamel Preservation
Regular dental check-ups are crucial for monitoring enamel health. Your dentist can provide personalized recommendations based on your specific needs. If you're experiencing tooth sensitivity or notice discoloration, don't hesitate to discuss it with your oral care professional.
In conclusion, understanding the impact of acidic food consumption on enamel integrity is vital for maintaining a healthy, white smile. By adopting these protective measures and being mindful of your diet, you can enjoy your favorite foods without compromising your enamel's well-being.
Links
- Please find a detailed article about teeth whitening on the ADA website.
- Tooth Whitening: What We Now Know on the National Library of Medicine website.
Discover our Sustainable Electric Toothbrush



Share:
Can You Bring An Electric Toothbrush on a Plane? (2024)
How often should you change your toothbrush?